The Impact of Software on Automotive Performance
Software has become an indispensable component in the modern automotive industry, fundamentally reshaping how vehicles operate, perform, and interact with their environment. From optimizing engine efficiency to enabling advanced driver-assistance systems, its influence extends across every critical function of a car. This evolution marks a significant shift from purely mechanical engineering to a complex interplay of hardware and sophisticated digital systems, driving advancements in safety, connectivity, and overall user experience.
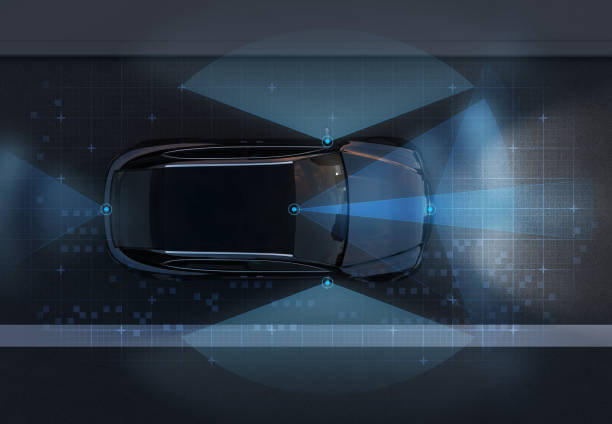
The automotive landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, largely driven by the increasing sophistication of software. What was once primarily a mechanical endeavor is now a highly integrated system where lines of code dictate everything from fuel injection timing to the responsiveness of steering and braking. This digital revolution is enhancing vehicle capabilities, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in terms of performance, efficiency, and user interaction.
How does software influence vehicle mobility and transportation?
Software plays a critical role in redefining mobility and transportation by enabling intelligent vehicle operation and seamless integration into broader ecosystems. Modern vehicles rely on software for engine management, transmission control, and chassis systems, all of which directly impact driving dynamics and fuel efficiency. For instance, sophisticated algorithms optimize combustion processes, leading to better power delivery and reduced emissions. In urban environments, software-driven traffic management systems and navigation tools help alleviate congestion, influencing the flow of transportation and individual journey planning. The continuous development of these systems is key to improving the overall efficiency and responsiveness of vehicles in various driving conditions.
What role does software play in electric and autonomous vehicles?
In electric vehicles (EVs), software manages critical components like battery thermal management, power delivery to electric motors, and regenerative braking, directly affecting range, charging speed, and performance. The efficiency with which an EV converts battery power into kinetic energy is largely a software optimization challenge. For autonomous vehicles, software is the central nervous system, processing vast amounts of data from sensors such as cameras, radar, and lidar. This software enables perception, prediction, planning, and control, allowing the vehicle to understand its surroundings, anticipate actions of other road users, and make decisions in real-time. The reliability and accuracy of this software are paramount for safe and effective autonomous operation.
How does software enhance automotive connectivity and safety?
Connectivity, powered by advanced software, transforms vehicles into mobile data hubs, enabling features like over-the-air (OTA) updates, real-time traffic information, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication. These connections facilitate proactive maintenance, enhance navigation, and support emergency services. Software also forms the backbone of modern automotive safety systems. Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS), such as automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assist, and adaptive cruise control, rely heavily on complex software algorithms to interpret sensor data and intervene when necessary. These systems significantly reduce the risk of accidents by providing warnings or actively assisting the driver, thereby improving overall road safety.
What are the implications of software in automotive design and manufacturing?
Software is integral to every stage of automotive development, from initial design to final manufacturing. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) software allow engineers to simulate and test vehicle components and full systems virtually, optimizing aerodynamics, structural integrity, and crashworthiness before physical prototypes are built. In manufacturing, robotics and automated systems, all controlled by specialized software, ensure precision, efficiency, and consistency on the assembly line. This integration of technology streamlines production processes, reduces waste, and allows for greater customization and rapid iteration of vehicle designs.
How does cybersecurity apply to modern automotive software systems?
As vehicles become more connected and software-defined, cybersecurity becomes a critical concern. Automotive software systems are vulnerable to various cyber threats, ranging from unauthorized access to malicious manipulation of vehicle functions. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect sensitive data, prevent hacking, and ensure the integrity and safety of vehicle operations. This involves implementing secure coding practices, encryption, intrusion detection systems, and regular software updates to patch vulnerabilities. The industry continually invests in developing advanced cybersecurity protocols to safeguard vehicles against evolving cyber risks, ensuring the reliability and trustworthiness of automotive technology and protecting user privacy and safety on the road.





